Indoor Air Quality: How Good is the Air Inside Your Home?

Many of us are conscious of outdoor air pollution and the health problems it can trigger. However, the air inside our homes often harbors more significant threats, with studies showing that indoor air pollution could be 10 times worse than the air outside. We will explore the factors influencing indoor air pollution and how you can measure air quality within your living spaces.
Key Points to Note
- Understanding Indoor Air Pollution: Indoor air pollution is a silent yet substantial health hazard for you and your loved ones. It can provoke allergies, but research also suggests links to severe health complications like cancer, hypertension, and high blood pressure.
- Identifying Sources of Indoor Air Pollution: A variety of contaminants can reduce your indoor air quality. Poor ventilation is the primary culprit, with household items, faulty HVAC systems, and exposure to natural gases from the earth's crust contributing to the problem.
- Determining Air Pollution Levels: Conducting a home air quality test can help you assess the level of pollution. You can either use a home test kit or hire professionals, each with their pros and cons.
How Do We Gauge Air Quality?
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool used to measure air quality, evaluating common pollutants such as airborne particles, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. The scale spans from 0 to 500:
- 0 - 50 (Green): Excellent Air Quality
- 51 - 100 (Yellow): Fair Air Quality
- 101 - 150 (Orange): Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
- 151 - 200 (Bright Red): Unhealthy for Everyone
- 201 - 300 (Purple): Very Unhealthy
- 301 - 500 (Dark Red): Extremely Hazardous
Though typically used to measure outdoor air quality through ground assessments and satellite technology, AQI can also gauge the air quality within your home.
Understanding the Effects of Poor Indoor Air Quality
The AQI quantifies pollutant levels in the air by determining the particulate count. The more particles there are, the worse the air quality is for your health. It's important to note that many of these harmful particles are minuscule and nearly invisible. An AQI over 100 indicates poor indoor air quality, which can vary throughout the day or week—think about the air after you've prepared a meal in your kitchen, for instance.
While the effects of poor air quality might not be severe in the short term, they can still cause allergies and respiratory issues like asthma and sinusitis. This risk is particularly acute for children, who face nearly double the risk of developing pneumonia from indoor air pollution. Long-term exposure, however, can lead to serious health problems like heart and respiratory diseases and even cancer. Long term exposure to poor indoor air quality is so detrimental that the World Health Organization attributes about 3.2 million deaths annually to indoor air pollution, earning it the moniker the "invisible killer."
Uncovering the Culprits of Poor Indoor Air Quality
- Lack of Ventilation: Poorly ventilated homes can trap polluted air indoors, reducing air quality. Proper ventilation—opening doors and windows—allows fresh air in and removes stale, polluted air.
- Cooking: Preparing meals, especially with a gas stove or oven, can significantly deteriorate indoor air quality by introducing natural gas and smoke into the air..
- Household Chemicals: Products such as cleaners, air fresheners, and furniture can release a variety of harmful substances.
- Radon: This toxic gas, found in the earth's crust, can seep into your home through the foundation.
- Inadequate Heating Systems: Gas and oil-powered stoves and furnaces emit air pollutants like sulfur and risk carbon monoxide emissions. Wood-burning fireplaces also release harmful substances. Temperature and Humidity: The health issues linked to poor air quality aren't solely due to airborne pollutants. Living in extreme temperatures can cause problems like poor sleep, heightened stress, and an increased risk of dehydration and heat stroke. A well-functioning HVAC system is vital for your comfort and health.
Classifying Indoor Air Contaminants
Air contaminants fall into three primary categories:
- Biological Pollutants: These include mold spores, bacteria, dust mites, and pollen. These contaminants can cause respiratory problems and asthma attacks, with mold posing more serious health issues if left untreated. Whole house purifiers can usually filter out these pollutants.
- Combustion Pollutants: Secondhand smoke from tobacco, marijuana, and other burnt substances can cause lung cancer over time. Carbon monoxide, a dangerous pollutant emitted by gas stoves, space heaters, and unvented kerosene, can lead to flu-like symptoms or even death. Having carbon monoxide detectors in your home is crucial.
- Chemical Pollutants: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) found in household items, lead found in older homes, formaldehyde prevalent in manufacturing glue used in furniture, and radon emanating from the ground all fall under this category. For radon, you can find short and long-term air quality test kits available online, or they might be provided by your city for free.
Exploring Major Contributors to Indoor Air Pollution
The factors that degrade indoor air quality are numerous, with the most notorious offenders listed below:
- Indirect tobacco smoke exposure
- Aerosols such as air fresheners, hairsprays, and adhesive sprays
- Household cleaning products
- Wood-burning fireplaces
- Pest control substances
- Heating appliances fueled by fossil fuels, including oil or gas-powered heaters, fireplaces, and stoves
- Candles and incense
- Off-gassing by items such as paint, flooring, and furniture
Implementing Home Air Quality Tests
To determine if you're dealing with subpar air quality at home, there are a variety of testing methods you can employ. Here's how you can assess your home's air quality:
- Use air quality monitors to test your air quality
- Investigate specifically for carbon monoxide
- Check specifically for radon
- Conduct a mold test
- Enlist professional air quality monitoring services
- Learn about the indicators and symptoms of poor indoor air quality
Utilizing Air Quality Monitors for Home Testing
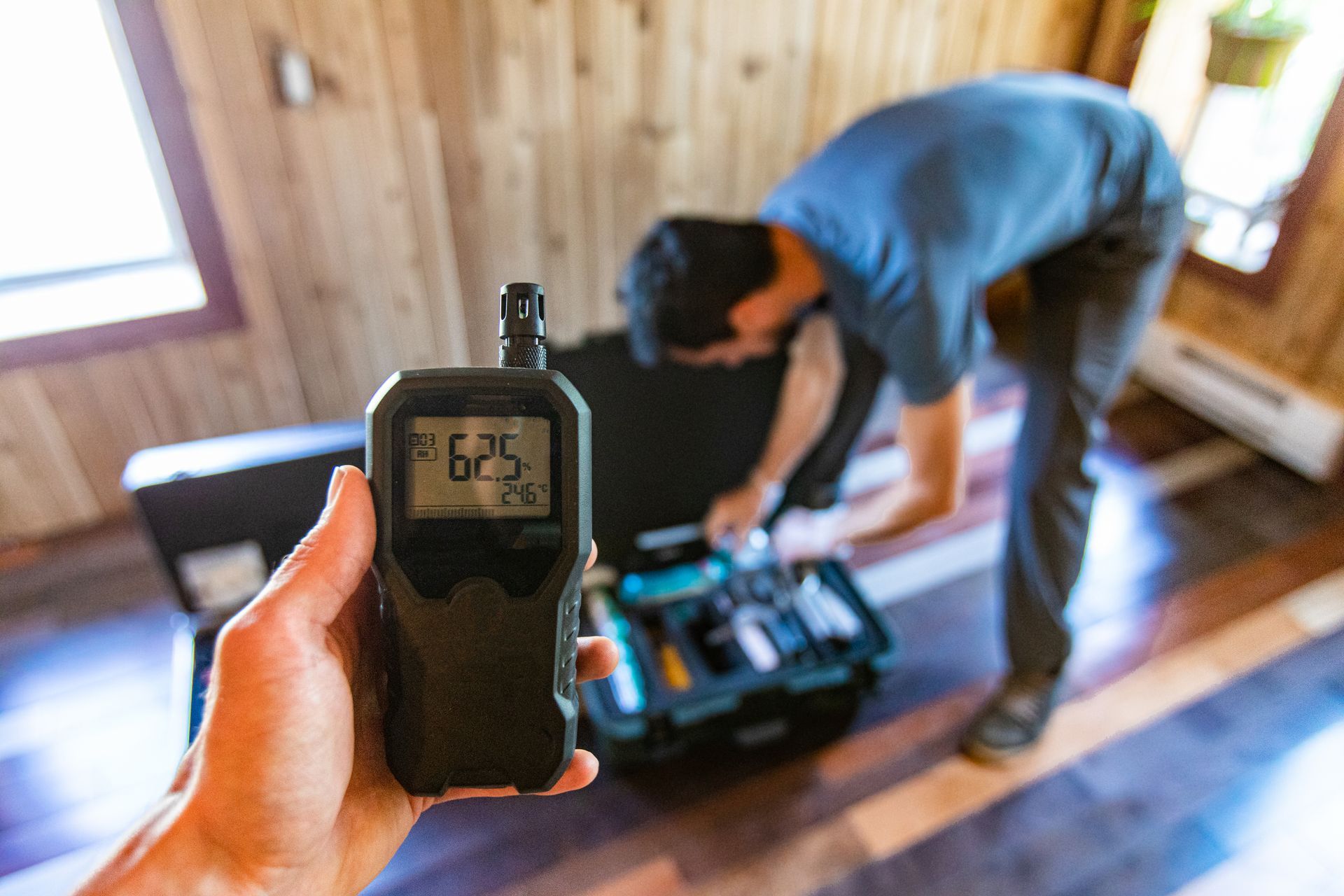
You can assess your indoor air quality using air quality monitors. These devices use electrochemical sensors to estimate particulate matter and detect toxins. They're available in diverse designs and price ranges, some being handheld and others suitable for wall mounting.
Not all pollutants can be detected by air quality tests, but an ideal model should be able to measure:
- Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Particulate levels
- Temperature and humidity
- Volatile organic compounds
If there's a specific pollutant that you're particularly worried about, you should get an air quality monitor designed to detect it.
Checking for Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide, one of the most dangerous gases polluting indoor air, is infamously referred to as the "silent killer" due to its colorless, odorless nature and its capacity to reach hazardous levels in poorly ventilated areas or during a gas leak.
Every home should have carbon monoxide alarms installed in areas similar to smoke detectors (e.g., outside bedrooms). These alarms, which cost between $10-$15, alert you to dangerous levels of carbon monoxide in your home. Some are battery-operated, while others require a plug-in power source.
Reducing minor carbon monoxide emissions can be achieved by swapping gas-burning stoves, fireplaces, and heaters with electric ones.
Investigating for Radon
As mentioned before, radon gas is a byproduct of uranium decay in soil. This gas can permeate upwards through soil and infiltrate your home via cracks in the foundation. To check if radon is polluting your home, you'll need an air quality test kit specifically designed for radon detection. The radon monitor should be placed in high-risk areas of your home, typically rooms at or below ground level.
Tests can be short-term (2 to 7 days) or long-term (up to 90 days or a full year). Regardless of the test duration, the monitor must be sent to a lab for results analysis.
Remember: air purifiers can't effectively reduce radon levels in your home. If your home has radon contamination, sealing gaps in the foundation is really the only effective way to mitigate it.
Testing for Mold
Tiny mold spores can pollute your indoor air, which a mold test can detect. These tests are relatively inexpensive, are available at home goods stores, and can alert you to overlooked mold infestations. Here are a few types of mold tests:
- Swab Tests: These allow you to sample surfaces in your home and provide quick results, though they can't identify the mold type.
- Tape Strips: These offer more accurate results but require lab analysis and can be easily contaminated.
- Petri Dish Tests: These kits may be prone to contamination, but they can confirm the presence of mold if it grows in the provided substance.
- Air Pump Tests: These tests offer accurate results with less likelihood of contamination, but they tend to be more expensive.
Mold removal can be hazardous without proper gear, so it's best handled by professionals.
Professional Air Quality Monitoring
If you're committed to enhancing your home's air quality, consider hiring professionals to test it. They can detect various pollutants and deliver quicker test results, along with advice on eliminating and preventing future air pollution.
Recognizing Poor Indoor Air Quality Signs
Sometimes, you might not need a monitor to realize your air quality is poor. Look for these signs:
- Health issues such as allergies, asthma, or other respiratory conditions
- Mold accumulation
- Excessive household dust
- Musty air and strange odors
- Older home materials deteriorating
- Cold air drafts
- Condensation on windows
- Unequal home temperatures
Tips for Better Indoor Air Quality
You can adopt simple methods to improve your indoor air quality:
- Boost Your Ventilation: Open your windows regularly for better ventilation. Also, ensure regular HVAC system maintenance to keep it efficient.
- Install an Air Purifier: This is an effective way to filter indoor air pollutants.
- Use Exhaust Vents: Use these in kitchens and bathrooms to remove humidity and pollutants. Keep your kitchen exhaust on for about twenty minutes post-cooking to combat pollution from gas stoves.
- Install Alarms: Install a carbon monoxide alarm as soon as possible for safety.
- Opt for Electric: Replace gas-powered and wood-burning heating sources with electric ones. This not only improves air quality but also enhances energy efficiency and saves money in the long term.
Contact Greener Solutions for Indoor Air Quality Issues
Reach out to us if you suspect poor indoor air quality in your home. We offer a range of air quality services for residential and commercial properties in Central California, where heat poses a higher risk of indoor air pollution. Our licensed professionals can check indoor air quality and install an air scrubber if results indicate poor indoor air quality.