AC Refrigerant: Types, Usage, and Best Practices

Refrigerant is a relatively unknown material that is critical in maintaining the normal operation of today’s society. This powerful fluid impacts every living person in some way or another. Some rely on it to keep their cars, homes, and businesses cool, others rely on it to keep their foods at a temperature that prevents the spread of food borne illnesses, while some rely on it to preserve their medications. Regardless of how you use refrigerants, there is no question that it plays an integral part in the normal function of society.
What is Refrigerant?
Refrigerants are the fluid chemical compound found inside of air conditioners and refrigerators that are responsible for the cooling powers that both appliances provide. These fluids cycle through these appliances and extract heat from one area and then transport it somewhere else using the power of thermal transfer and evaporation. This is all possible due to how refrigerants can change between their liquid and gas phases with the help of mechanical engineering and applied pressure.
What Does Refrigerant Do?
The simplified process of what refrigerant does can be summed up as it collects heat from one space and then releases it somewhere else. The more detailed explanation requires an little knowledge of air conditioners and their internal components. Refrigerants are contained inside of the internal components found within AC units and refrigerators where it cycles through the system repeatedly. The following steps detail how refrigerant cycles through the evaporative process:
- The refrigerant exists in its liquid state inside the copper evaporator coils
- The liquid refrigerant begins to evaporate as heat from a room transfers into the cool liquid
- The pressure from the evaporated refrigerant sends the heated gas out to compressor
- The compressor pressurizes the gas to superheat it before sending the gas out to the condenser coils to cool
- The superheated gasses reach the condenser coils where the fan will blow away the radiant heat
- This prompts are rapid drop in temperature which initiates the refrigerant phase change back into its liquid form
- This cooled liquid refrigerant gets returned to the evaporator coils where the process starts again
How Refrigerant Has Changed
The first refrigerant that made it to market was back in 1928 under the name Freon, which became synonymous with refrigerants at the time. The primary element found within freon were chlorofluorocarbons which were found to be extremely damaging to the ozone layer. This material was eventually phased out in 1995 after immense public outcry. After the legacy version of Freon was phased out, it was replaced with R22. R22 still contained CFCs but the lifespan it spent in our ozone layer was severely reduced which was a slight improvement from the legacy Freon. This was also eventually banned and units that rely on R22 were phased out in 2010 which production of R22 stopped altogether in 2020. After the ban on R22, a new refrigerant was needed to power HVAC units around the world. This prompted the creation of R410A, also known as Puron.
Types of AC Refrigerants
Due to certain refrigerants being phased out, the creation of other refrigerants was needed to fill the void left by the discontinued classes of refrigerants. It is important to know that different classes of refrigerants are not interchangeable and cannot be swapped out for another.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) – CFCs were the original class of refrigerants which were responsible for the hole in the ozone layer environmental disaster that made headline news in the 80’s and 90’s. These refrigerants included R11, R12, and R115. These materials were eventually banned by the EPA and then the rest of the world before being phased out in 1995.
R22 or Freon 22 – Following the ban on Freon, R22 became the popular substitute. This wasn’t a perfect fix to the ozone depletion problem but it was a step in the right direction. This chemical had the same ozone depleting capabilities as CFCs but there was an additional hydrogen atom that was introduced that drastically reduced the CFC’s lifespan in our environment. This substance was also eventually banned by the EPA.
R410A or Puron – As R22 products were phased out, a replacement was needed to fill the void. R410A became the standard for refrigerants. R410A is far less damaging to the environment while still maintaining its ability to cool. It has higher cooling efficiency which decreases power consumption when being used.
R32 – R32 products are the next generation of efficient low impact refrigerants. R32 has a GWP metric that is 32% of R410A.
What Changes in Refrigerant Legislation Means for HVAC Owners
Since HVAC units can last between 15 - 30 year, it is very possible that older systems that still rely on R22 exist and are actively being used. The changes in legislation that dictate what refrigerants are acceptable impact how homeowners that have R22 reliant HVAC systems should move forward. For homeowners that had their HVAC systems installed before 2010, it is possible they are using R22 reliant HVAC unit. If that is the case, recharging R22 can only be done using recycled or reclaimed R22. It is not required that R22 units be replaced but homeowners should weight the costs of maintaining an outdated system that requires the use of increasingly expensive refrigerant.
The Future of Refrigerants
Even R410A isn’t perfect and can be improved upon. The most recent refrigerant to hit the market is R32. This refrigerant class has even lower energy consumption and smaller environmental impact. Studies on the product have indicated that the Global Warming Potential (GWP) of R32 is 32% of the GWP of R410A. GWP measures the level of emissions that are contributed during the manufacture and distribution of a product. The other benefit of transitioning to R32 is that newer efficient HVAC units are being created to operate with R32 as its refrigerant source. These units rely on as much as 20% less R32 due to how efficient and effective it is.
How to Tell Which Refrigerant an AC Unit Uses
Knowing when your AC unit was installed is typically the easiest way to determine what refrigerant your AC needs. Units that were installed before 2010 mostly relied on R22 while units installed after 2010 rely on R410A or R32. The newer your unit is, the more likely it is to rely on R32. The most accurate way to determine what refrigerant you need is to check the appliance description sticker on the exterior HVAC unit or user manual. Any documentation related to the HVAC should provide details that are relevant to AC maintenance and refrigerant recharging.
When Do You Need to Refill AC Refrigerant?
Healthy air conditioner operation relies on maintaining refrigerant levels. If refrigerant runs low, the effectiveness of your AC unit drops, which increases the air conditioner’s workload. This results in increased energy costs and higher levels of wear and tear. It’s important to know that refrigerant shouldn’t need to be topped off regularly unless there is a leak in the system. The system is part of a closed loop that shouldn’t release any refrigerant over time. Refrigerant levels can be checked annually as part of regular AC maintenance and if any refrigerant needs to be recharged, the system should be checked for refrigerant leaks.
Signs Your AC is Running Low on Refrigerant
If your AC unit develops a leak, it’s only a matter of time before refrigerant levels run low. When this occurs, there are a few signs to look out for.
- AC not producing cool air
- Frozen evaporator coils
- AC running constantly
- Increased energy bills
What’s the Solution to an AC Refrigerant Leak?
AC refrigerant leaks are a common occurrence that are relatively easy to diagnose and repair if caught early. It’s only when they go unnoticed and cause stress on other components to the point they fail that they cause a serious problem.
System Assessment
An air conditioner that is unable to cool an area effectively should be inspected by a professional HVAC technician to ensure that the problematic component is identified. The technician will inspect the different elements that the refrigerant passes through to determine if and where a leak exists.
Locating Refrigerant Leak
The different components that will need to be examined thoroughly include the evaporator coils, condenser unit, or refrigerant lines.
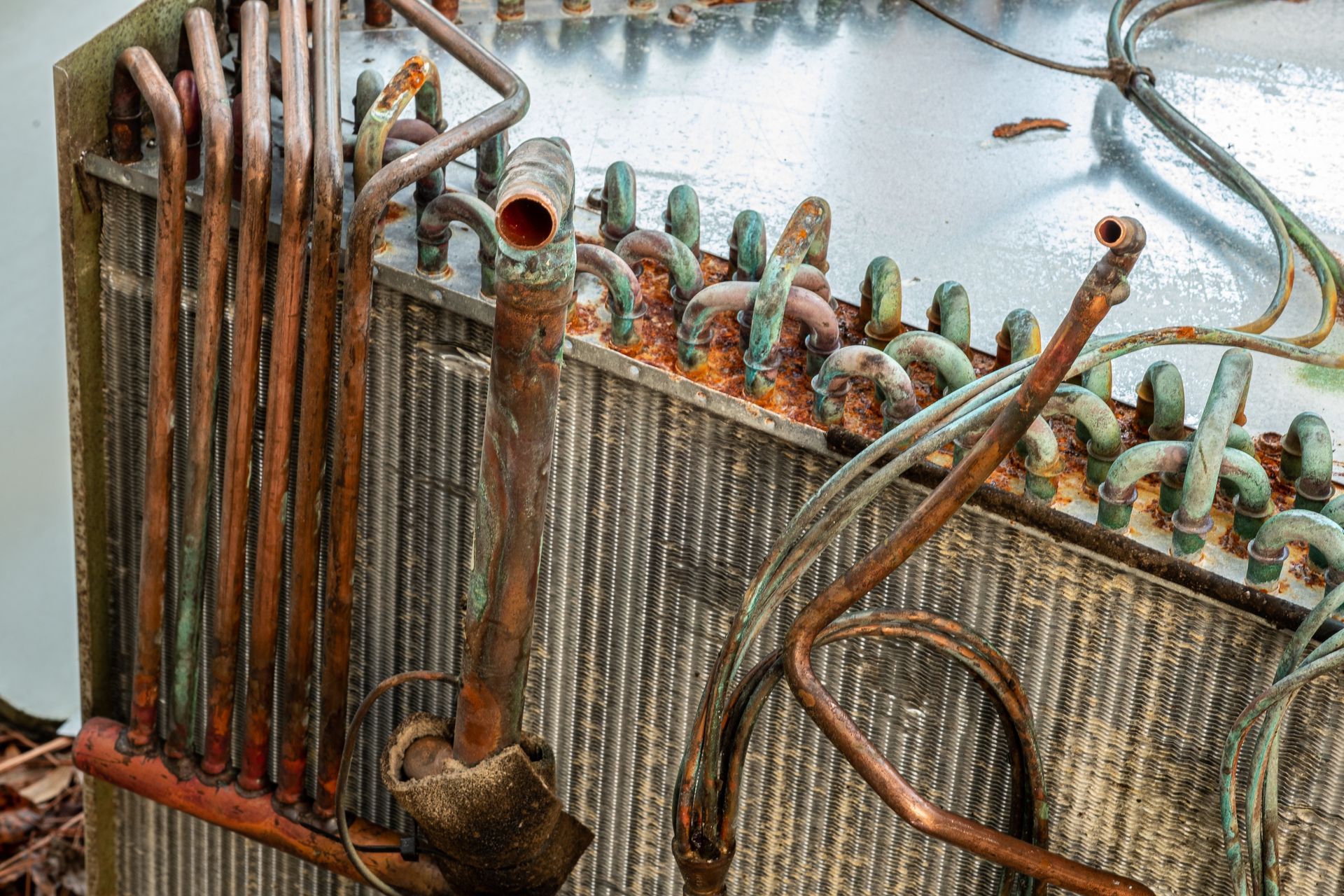
- Evaporator coils: These coils are the most common place for a refrigerant leak to occur. These coils are responsible for absorbing heat during the phase change so when the liquid refrigerant evaporates, the increase in pressure can cause the gas to escape from small pin sized holes.
- Condenser unit: This outdoor unit gets a lot of abuse from wind, rain, and other elements which can result in corrosion which leads to leak in the refrigerant line.
- Refrigerant lines: These lines are the components that connect the coils to the different mechanical parts that help move the refrigerant through the HVAC system. These parts are susceptible to springing leaks.
Most leaks can be discovered using the “soap bubble” test where holes are identified by bubbles that appear when a soapy water mix is applied to the surface of damaged component.
Determine the Type of Refrigerant
Once a leak is discovered, the refrigerant levels will need to be restored back to optimal levels for the HVAC system to work properly. Determining the correct type of refrigerant is extremely important because the different refrigerants are not interchangeable. Using the incorrect refrigerant will break the compressor causing the entire AC unit to fail.
Repair Leak
Repairing a refrigerant leak can sometimes be as simple as applying an adhesive sealant to the hole. Other times it can require entire components be replaced. This means that the cost of repairs will most likely be dependent on severity and location of the leak.
Refrigerant Recharge
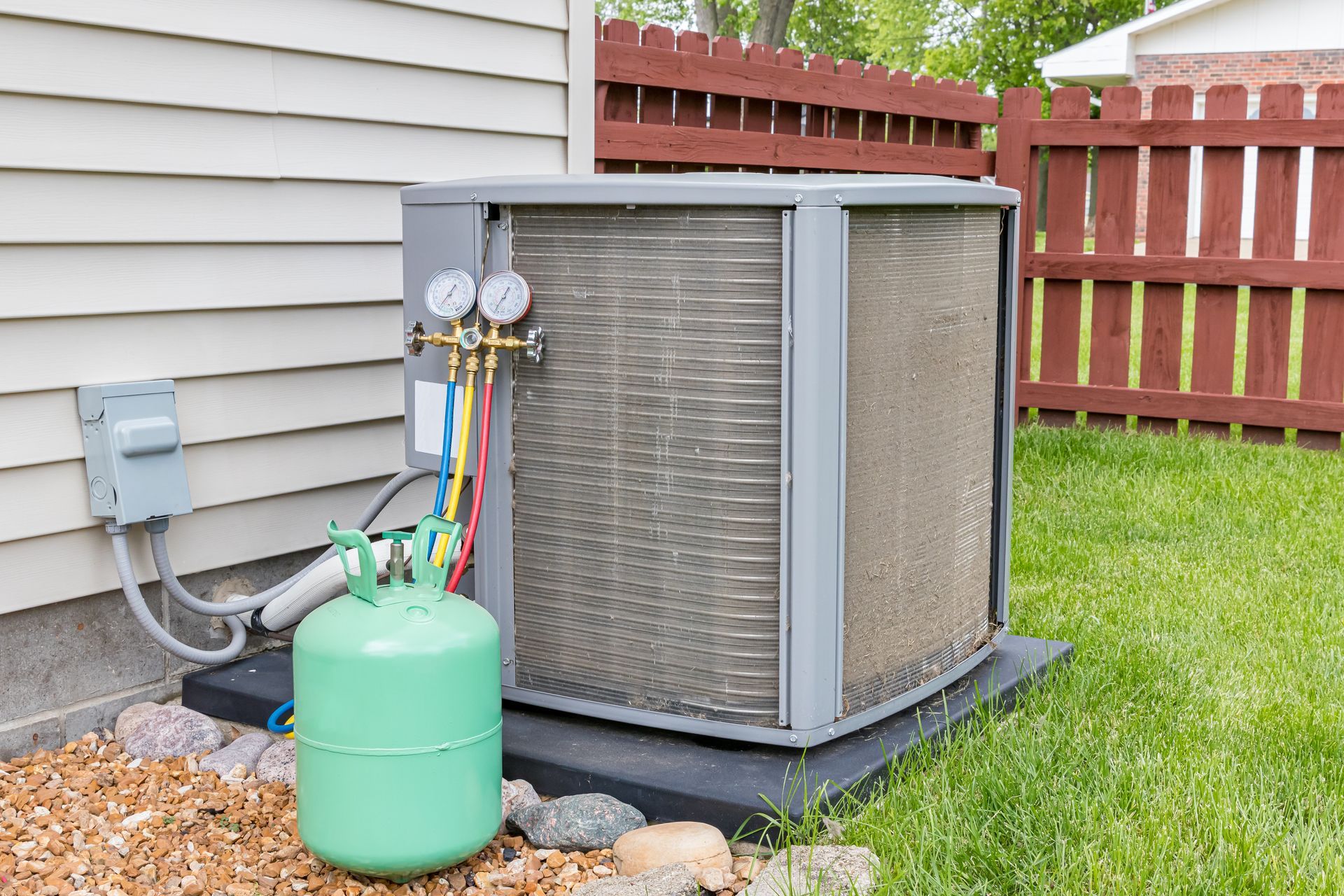
After the damaged leaking part has been replaced, it is critical to remember that the refrigerant levels need to be restored. This should always be done by a professional who is licensed to use refrigerants and trained and qualified to work with pressurized gasses. This is particularly true for older units that rely on controlled refrigerants that are no longer in production.
How Long Does an AC Refrigerant Refill Take?
Refilling AC refrigerant doesn’t take that long. Most AC units range between 1 – 5 tons with each system needing about 3 pounds of refrigerant per ton of AC unit. That means that most AC units will require between 3 – 15 pounds of refrigerant to be at optimal levels. Generally, it takes 5 – 10 minutes to charge one pound of refrigerant with most units needing 2 – 4 pounds when they run low. This means that to fill an AC unit it could take between 15 – 30 minutes for smaller units and 75 – 150 min for larger units. A simple recharge could take between 10 – 40 minutes.
Do You Need to Recharge Your AC Refrigerant Regularly?
AC refrigerant should operate within a closed loop system, so it does not need to be charged regularly. The rate at which refrigerant is lost requires that refrigerant levels typically be recharged every 2 – 5 years. The only reason refrigerant levels should drop noticeably is if a leak exists in the system. If there are any signs that refrigerant levels are low, then the lines should be checked for leaks first and repaired before being recharged.
Contact Greener Solutions If You Need Refrigerant Services
If you are dealing with refrigerant problems or reduced AC efficiency, it may be time to call on the help of professionals. Greener Solutions has a team of qualified and licensed HVAC technicians who are ready to come inspect your AC and refrigerant lines to determine if there is a problem or leak somewhere in your system. Call today to schedule an inspection and get your AC problem repaired.
AC Refrigerant FAQ
-
What refrigerant is used for AC?
Refrigerant is responsible for the exchange of heat that occurs during the operation of an AC unit. Using the process of evaporation, the refrigerant is able to collect heat from inside a space and move that heat to a new location where it can be dispersed.
-
Is R410A being phased out?
R410A isn’t being phased out by current laws and regulations yet, but R32 has been developed which is a far superior product. It is only a matter of time before R410A becomes obsolete and phased out.
-
What is R-22 and R32 in AC?
R22 is an antiquated refrigerant that is no longer being produced due to high levels of chlorofluorocarbons that it contained which were damaging to the environment. R32 is the most recent class of refrigerant to be introduced that is much more environmentally friendly and efficient.
Recent Posts
-
Our Services
ButtonSee All Our Services
-
About
ButtonLearn More about
Greener Solutions
-
Contact Us
ButtonImmediate Service
Emergency Services
Live Support
Have an HVAC emergency? Call for immediate service. Available 24/7